Here are some useful things to know about the Windows Registry:
What is the Registry?
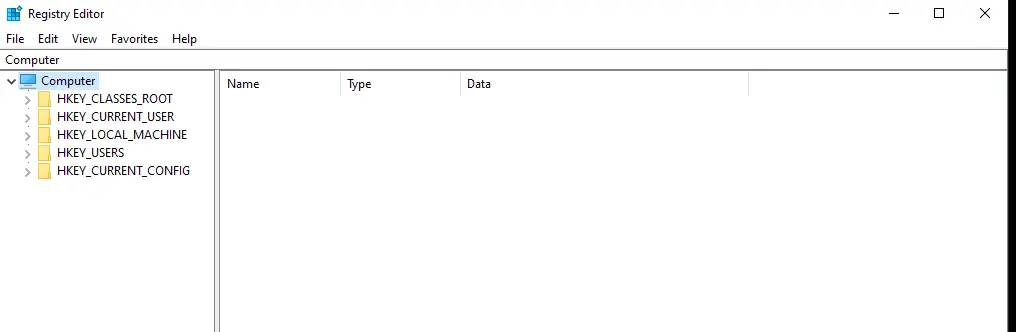
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database storing configuration settings and options for the OS, applications, and hardware.
Structure:
It’s organized into keys (folders) and values (data inside keys).
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- HKEY_USERS, HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG
are the main root keys.
Editing the Registry:
You can edit the registry using the Registry Editor (regedit), but caution is required—wrong changes can break the system.
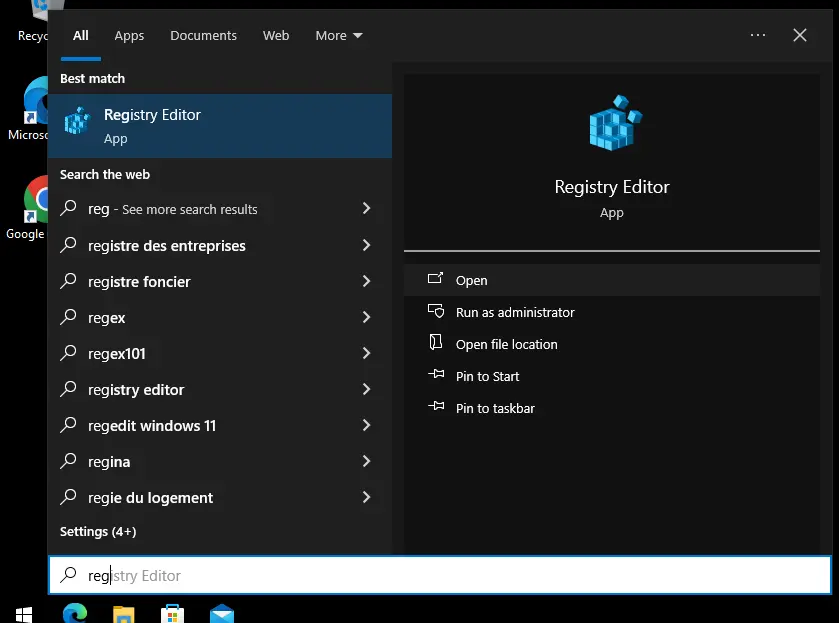
To open regedit you can go into your search bar and type regedit and press enter
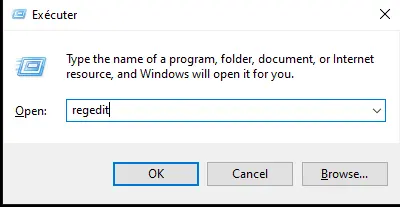
or you can do WIN + R type regedit and press enter.
Backup Before Editing:
Always back up the registry before making changes to avoid system issues. Right-click a key and select Export.

You can also make a backup of the whole registry if you go into file and export it.
Searching the Registry:
Use Ctrl + F in regedit to search for specific keys or values.
Registry Files:
The registry is stored in files with extensions like .hiv for system settings (found in C:\Windows\System32\config).
Regedit Commands:
regedit /s filename.regregedit→ This is the Windows Registry Editor command./s→ This runs the command in silent mode, meaning it will import the registry file without showing any confirmation prompts.filename.reg→ This is the registry file you want to import. It must be a valid.regfile containing registry keys and values.
regedit /e filename.reg "key"regedit→ Opens the Windows Registry Editor./e→ Exports the specified registry key and its values.filename.reg→ The output file where the exported registry data will be saved."key"→ The specific registry path you want to export. (Make sure to use quotes if the path contains spaces.)
Example
To export the Run key (which contains startup programs) from the Windows Registry, you would run:
regedit /e C:\backup\run_key.reg "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run"This will save the registry key and its values into C:\backup\run_key.reg. You can later import it back using:
regedit /s C:\backup\run_key.regTo use these commands, you must do it from either PowerShell or CMD.
Registry Cleaning Tools:
Use with care: Tools like CCleaner can remove invalid registry entries, but might cause issues if misused.
Remember, always be cautious while modifying the registry.